Lake Mead National Recreation Area
Near Las Vegas, Nevada – January 6, 2024
Impounded behind the concrete and steel of the magnificent Hoover Dam, Lake Mead in southeastern Nevada and southwestern Arizona is, by volume (and when full), the largest inland reservoir of water in the United States. There are a couple of U.S. reservoirs that have a larger surface area, but they don’t have the depth of Lake Mead (when full). The reservoir, made by the result of damming the Colorado River, is the primary feature of Lake Mead National Recreation Area – the nation’s first NRA as well as its largest at 1.5 million acres, or just over 2,400 square miles. For perspective, Lake Mead NRA is a couple hundred square miles larger than Kit Carson County in far eastern Colorado.
When full, Lake Mead has a surface area of 247 square miles, a surface elevation of 1,229 feet above sea level, and a maximum depth of 532 feet. When it’s full.
Lake Mead is, at the moment, not full. Not even close, really. In fact, it’s a couple hundred feet below its capacity, and it hasn’t been this empty since it was first filled after the construction of the Hoover Dam in 1937. A multi-decade-long drought in the southwestern United States, as well as unprecedented demand for agricultural and municipal water in the multi-state region served by the reservoir, have led to a stunning drop in the water level of Lake Mead. The reservoir’s capacity is so large that one inch of water in the lake equates to about 2 billion gallons. Two billion multiplied by 2,400 inches (200 feet) means Lake Mead has 48 trillion fewer gallons of water since the reservoir was last full in the mid-1980s. That number is so large as to be effectively useless, but in terms of acre-feet (which is the amount of water needed to cover an acre with 12 inches of water), Lake Mead is currently a little over a quarter of its capacity.
Geologists and hydrologists, along with other concerned -ogists, are working, and have been working for several decades, to address this issue. Many millions of people rely on Lake Mead’s water to continue flowing through the reservoir, providing electricity as well as drinking, municipal, and agricultural water. Mother Nature, while a powerful force in her own right, will take a long time to refill the reservoir: even after the remarkable upstream snowpack of the 2022-2023 winter in the Rocky Mountains, the reservoir rose only a few inches. It would take many consecutive decades of consistently above-average snowpack to refill the lake. That’s highly, highly unlikely to happen.
While the situation awaits a hopeful solution, that change in Lake Mead’s water levels also presents new opportunities for recreation: the receding water has left behind areas for great hikes. Recreation managers have developed at least 14 hiking trails all around the area, ranging from short and easy strolls to a 34-mile-long bike loop to strenuous hikes that are meant for the truly hardy among us.
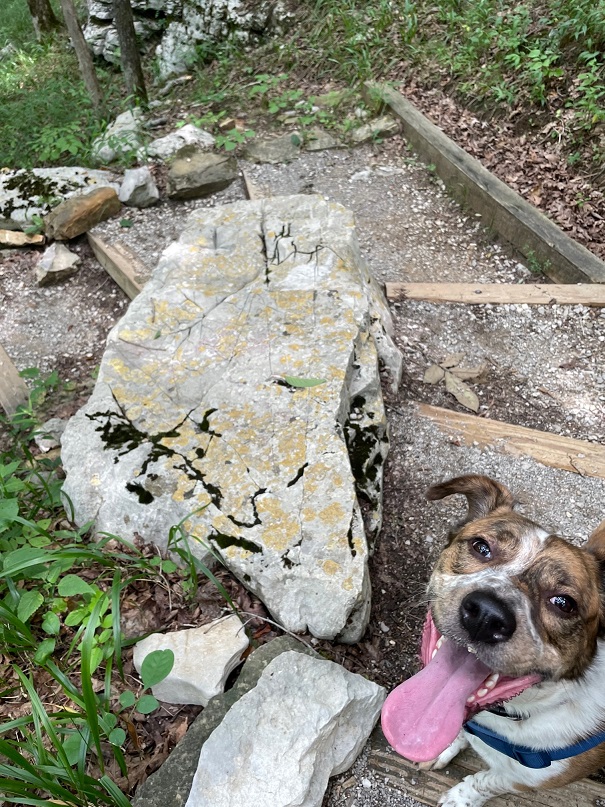
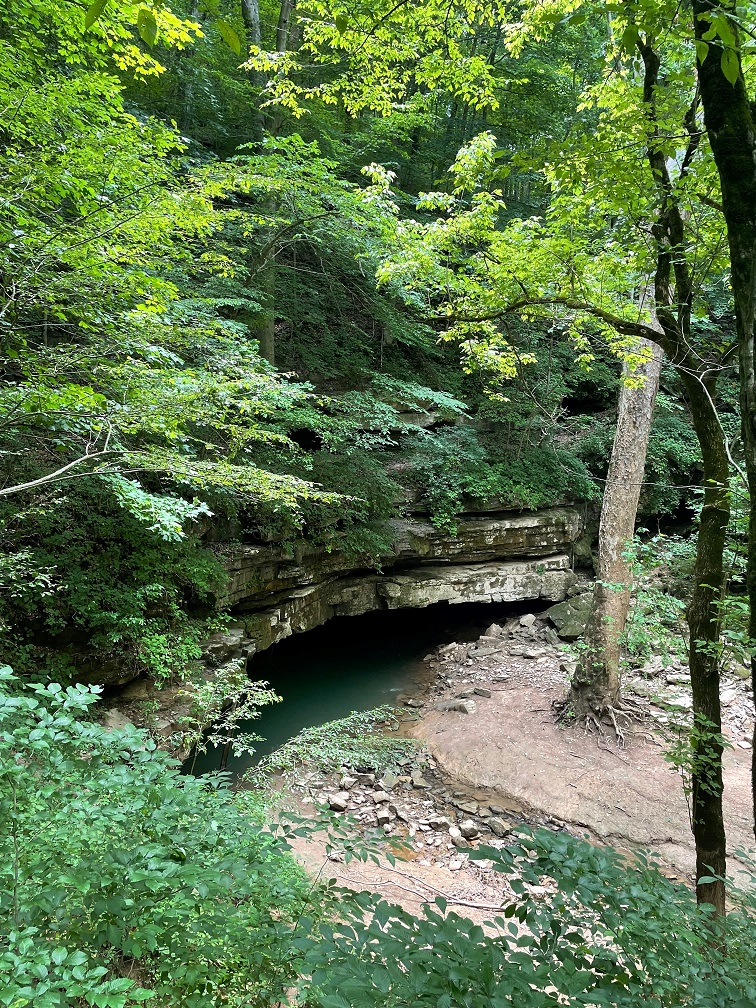
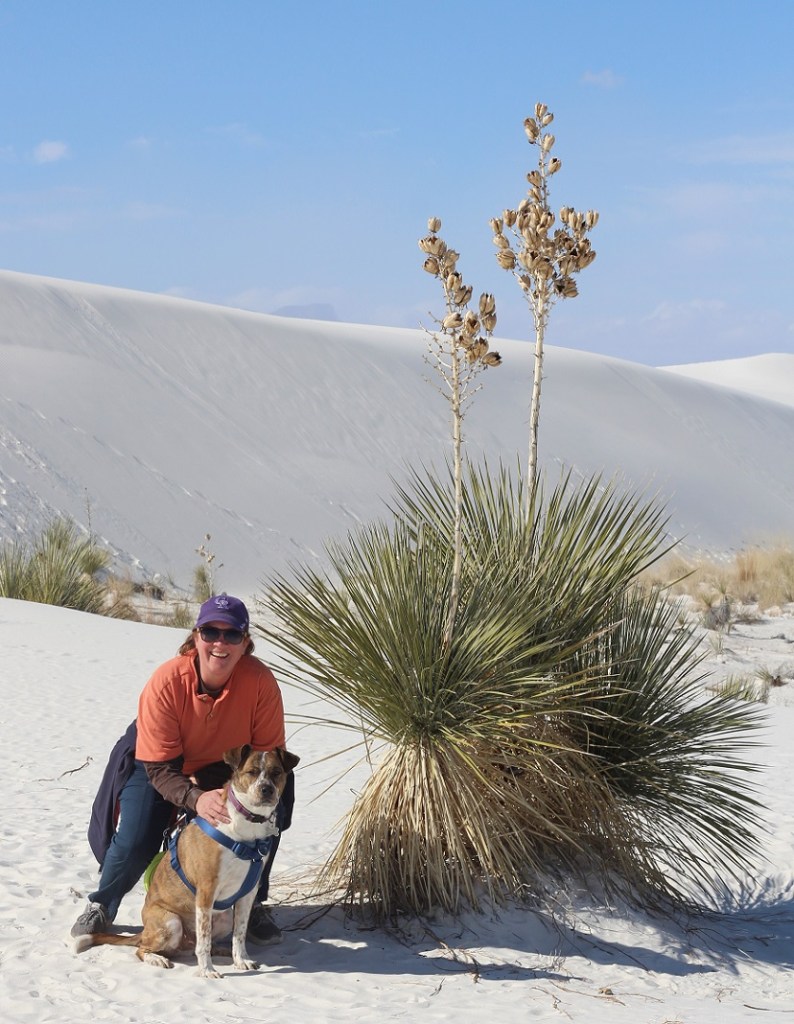
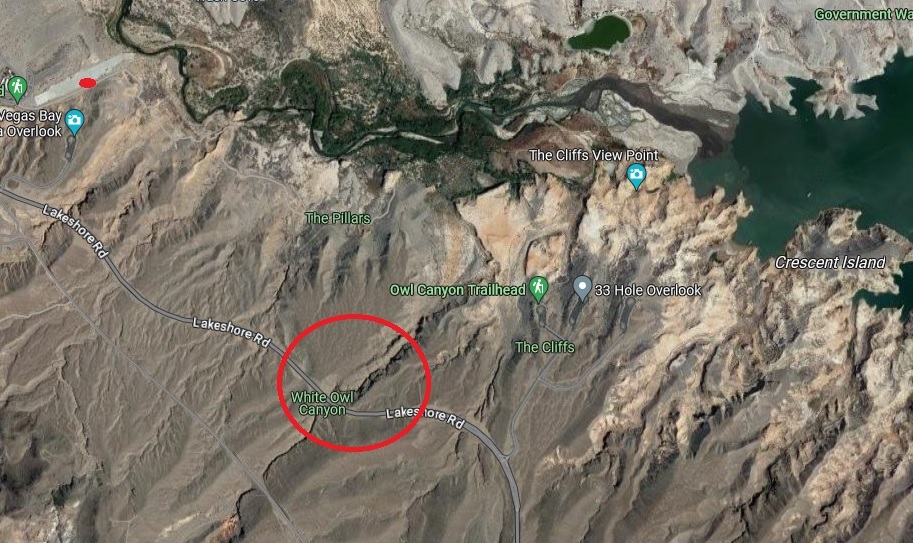
Which neither Nancy, nor Gunther, nor I, are. We lucked into a great hike called the Owl Canyon trail on the first weekend of 2024, and saw some pretty cool sights while enjoying a 4-mile out-and-back trail.



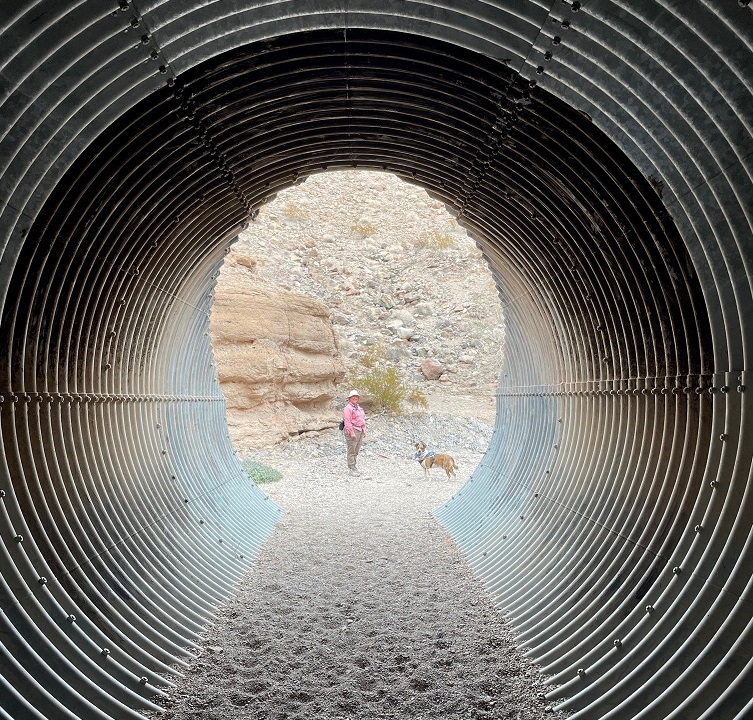
Here we see an intrepid hiker and her ill-behaved dog (it’s Nancy and Gunther) approaching the mouth of Owl Canyon, about a mile and a half from the trailhead on the boat ramp to the west. The canyon can also be accessed by a trailhead resulting in a shorter hike (2.2 miles out and back) coming from the northeast, but we wanted a bit more of a challenge for this first hike of 2024.
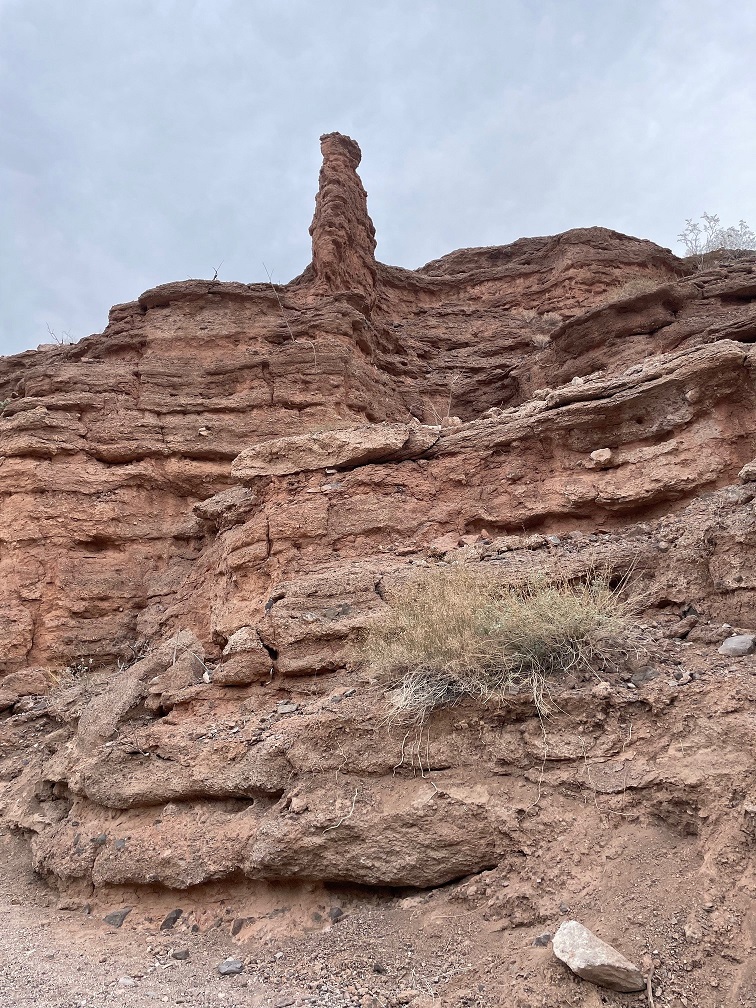
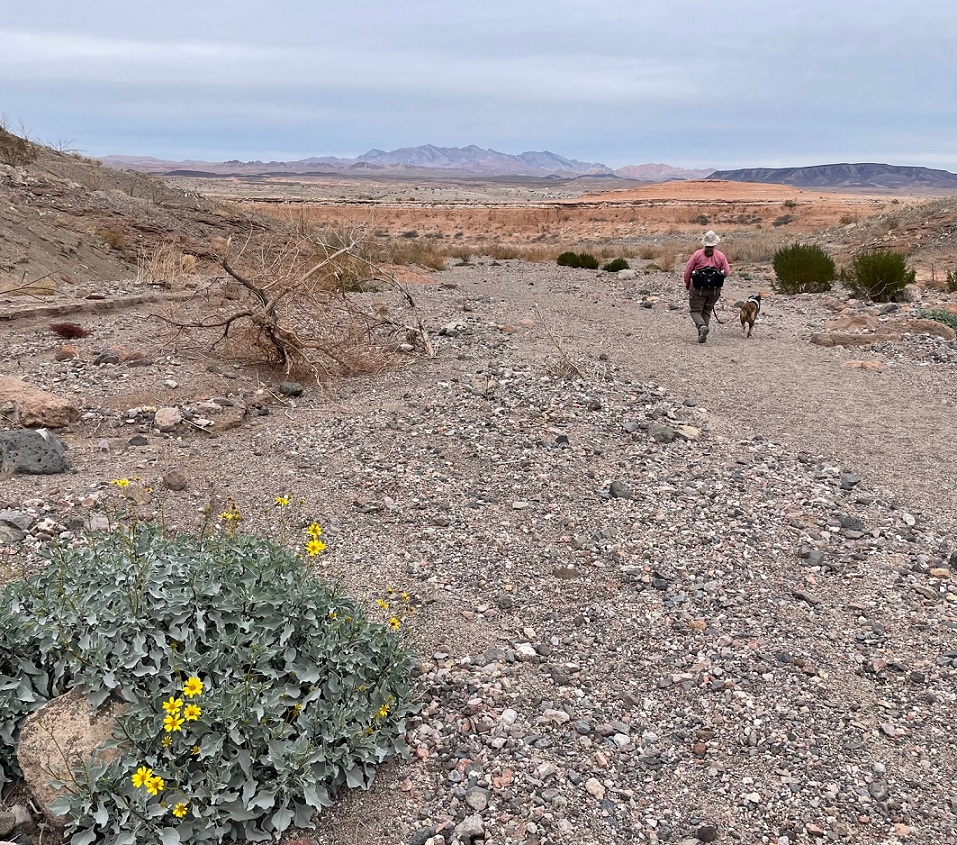










It’s easy to think that it’s not the end of the world if Lake Mead continues to dry up: the Colorado River flowed freely through this area for millions of years, supporting all kinds of native plant and animal life. But that’s not the world in which we currently live, and the disappearance of Lake Mead would be an absolute catastrophe: without constant flowing water to turn Hoover Dam’s turbines, many metropolitan areas in the southwest, like Phoenix, Las Vegas, and Los Angeles (to say nothing of the many thousands of smaller cities in the region), would suffer calamitous losses of electricity as well as a reliable source of water. Simply put, water impoundments like Lake Mead (and, to lesser but still vital extents, Lake Powell and Blue Mesa Reservoir upstream) make habitation of the southwest possible. Ain’t nobody living in Phoenix or Las Vegas in the 120-degree temperatures of July without air conditioning provided by electricity, to say nothing of being able to turn a faucet and expect water to come out.
It’s sobering to think that every step we took on this hike was once well underwater in Nancy and my lifetimes. Fortunately, smart and committed people are working on ways to continue developing and encouraging water conservation in the American southwest, but committed people will also need to actually take those steps in order to keep water flowing through Lake Mead.